In brief
- Ethereum rollups "roll up" a bunch of transactions into one.
- They come in two basic forms: optimistic rollups and zero-knowledge rollups.
Even after the latest crypto crash, Ethereum remains expensive for many to use. That’s because the Ethereum blockchain is slow and has maxed out its capacity. Now you must pay through the nose for every additional byte of block space if you are to buy the next "must-have" NFT.
Until "Ethereum 2.0," the next generation of the Ethereum blockchain, resolves all of these issues, the community must rely on so-called scaling solutions: technology that speeds up the Ethereum blockchain. Scaling solutions differ, but generally settle part of the transaction on another network—one faster and cheaper than Ethereum—before providing the main Ethereum chain with information about the transactions it plans to submit.
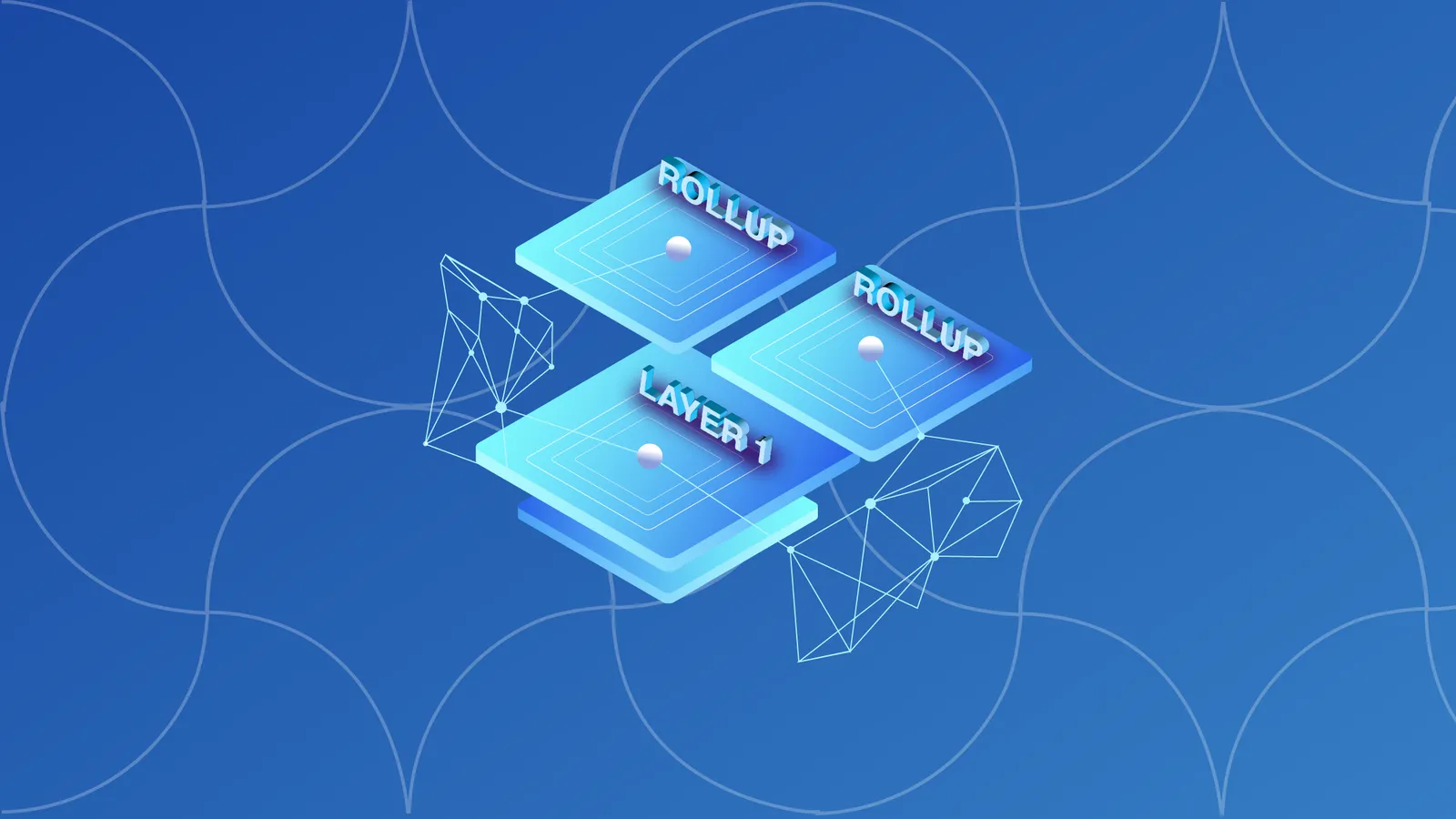
What are rollups?
Rollups are one such scaling solution. They involve rolling up (hence the name) collections of transactions. The final, rolled-up transaction is presented to the Ethereum blockchain as a single transaction.
Rollups cuts costs: the cost of an Ethereum transaction, plus the small cost of rolling up batches of transactions, is split among users. They also speed things up: the rollup is very quick to perform and the Ethereum blockchain needs only to process a single transaction rather than many. That's useful when Ethereum maxes out at around 15 transactions per second unassisted.
Vitalik Buterin, Ethereum’s co-founder, thinks that scaling solutions like rollups will continue to play an important role on the blockchain even after the implementation of Ethereum 2.0. (Note: The Ethereum Foundation has since dropped the 2.0 tag to refer to the network's move to proof of stake and adoption of shard chains.)
How do rollups work?
There are two main types of rollups: optimistic rollups and zero-knowledge rollups.
Optimistic rollups make the assumption that all of this rolled-up data is valid, and that nobody is trying to fool the blockchain by hiding spurious transactions within rollups. The idea is that by assuming validity, things speed up. To protect against fraudulent transactions, optimistic rollup protocols allow people to contest bunk trades. The fraudulent transaction is submitted directly on the Ethereum network to check if it’s legit, and to settle the dispute. Both parties have ETH staked and would lose money if they are wrong or lie.
Zero-knowledge rollups (also referred to as zk-rollups) work very differently. They rely on a piece of cryptography called a zero-knowledge proof, which allows someone to mathematically prove that a statement is true (that someone is, say, Greek) without disclosing additional information about that statement (like a passport). In crypto, these are called zk-SNARKs, in reference to an additional piece of cryptography called "succinct non-interactive argument of knowledge." This method bypasses the dispute-resolution system inherent to optimistic rollups because the "SNARK" bit only permits valid transactions to be uploaded to the rollup.
Who’s building rollups?
Optimistic rollups:
- Optimism: a cheap layer-2 system for Ethereum
- Arbitrum: an L2 protocol for Ethereum
- Boba Network: the next generation of OMG Network
Zero-knowledge rollups:
- Loopring: a protocol that also provides a gas-free decentralized exchange
- Immutable X: an L2 protocol for NFTs
- ZKSync: a zero-knowledge L2 for Ethereum
How can you buy rollups?
You can’t "buy" a scaling solution, but you can invest in tokens that rely on the technology. Loopring and Boba are popular examples of rollup technologies. You can buy their tokens on Ethereum-based decentralized exchanges or on centralized exchanges. Check sites like CoinMarketCap or CoinGecko to find the largest markets.
You can also use the DeFi services and exchanges created by these layer-2 networks to cut transaction costs. Loopring, for instance, operates its own layer-2 exchange, also called Loopring. There, you can take advantage of all of the delights of rollup technologies: gas-free, instantaneous trades for ERC-20 coins.
Did you know?
Rollups are just one scaling solution. Another common solution is called a sidechain—a blockchain that’s compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine, which connects to Ethereum through a bridge. An example of a sidechain network is
Polygon (formerly MATIC).
The future of rollups: a technology for the ages or a Band-Aid to a resolvable problem?
In the short term, the battle will continue to rage between the two competing forms of rollups: optimistic and zero-knowledge. Some claim that zero-knowledge proofs are superior because they do not require a dispute-resolution mechanism.
The long-term future of rollups depends on how upgrades to Ethereum’s mainnet pan out. Ethereum could one day become so fast that rollups would look like an unnecessary speed boost to a lightning-fast blockchain. Conversely, rival L1 blockchains, like Solana and Avalanche, could become so popular that they usurp Ethereum entirely. Should the majority of DeFi’s traffic take place on blockchains other than Ethereum, rollups would become redundant.
Alternatively, rollups could continue to rise should Ethereum become more powerful. They could integrate with the upcoming upgrades to make Ethereum easier and cheaper to use for the masses.